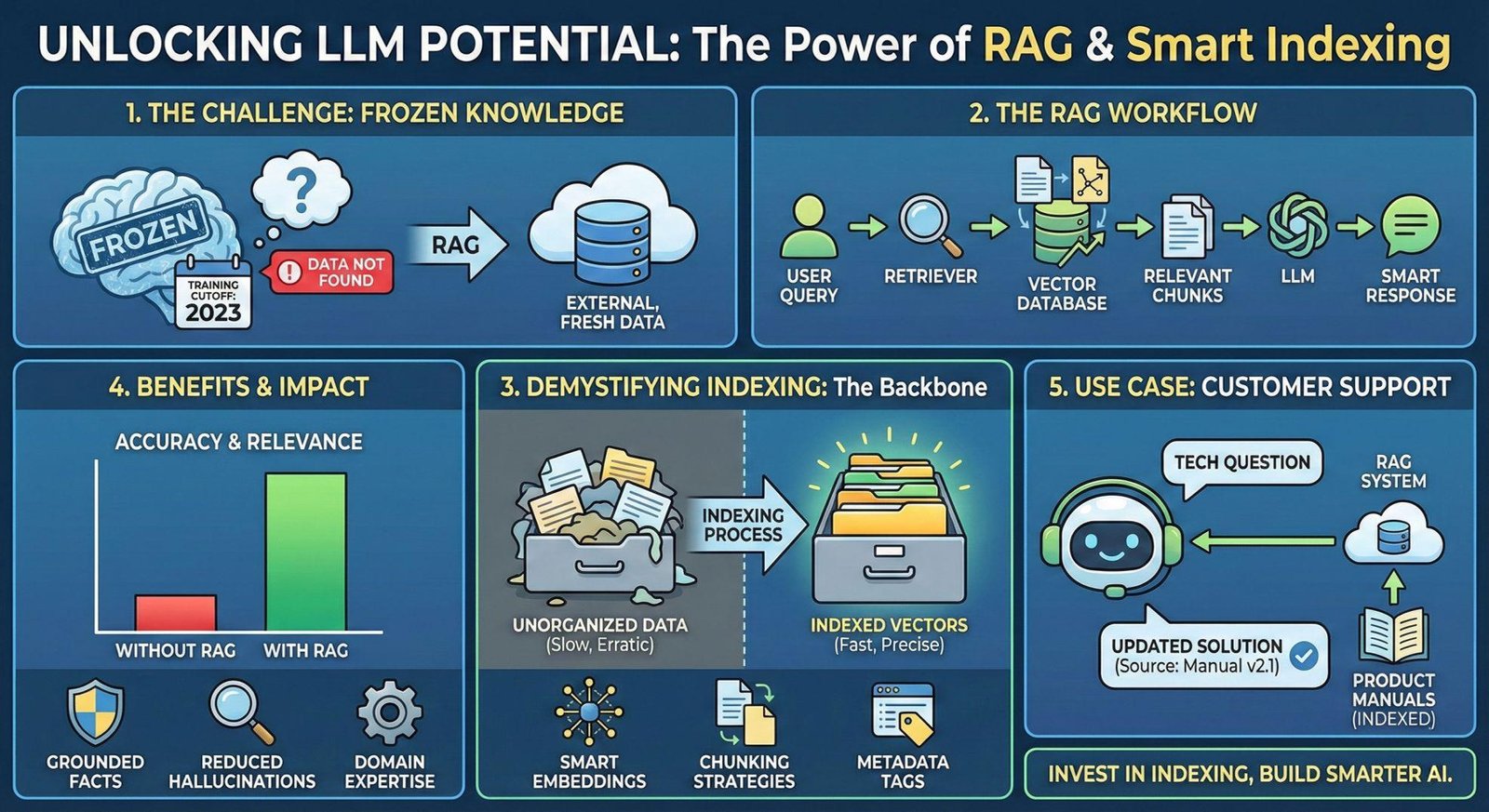
Understanding the Challenge: How Do LLMs Access External Knowledge?
Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 have revolutionized natural language processing, generating remarkably coherent and contextual text. But as powerful as they are, one major limitation remains: their knowledge is fixed to the data seen during training, which usually has a cutoff date. How can they tap into up-to-date or highly specific information outside their trained dataset? This is where Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) steps in. However, despite its rising popularity, many developers misunderstand the integral process of RAG Indexing — confusing it as just a fancy document-retrieval trick. It’s time to clarify these concepts and unlock RAG’s true potential.

What Exactly is RAG?
RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It’s an AI technique that combines a retriever mechanism with a large language model, enabling the model to fetch relevant information from an external source — such as a database or a vector store — and then use that information to generate more accurate and context-rich responses. Think of it as a researcher pulling up reference books before answering questions rather than relying solely on memory. While retrieval is intuitive to understand, many tend to stumble at the idea of indexing, which forms the backbone of a smooth retrieval process.
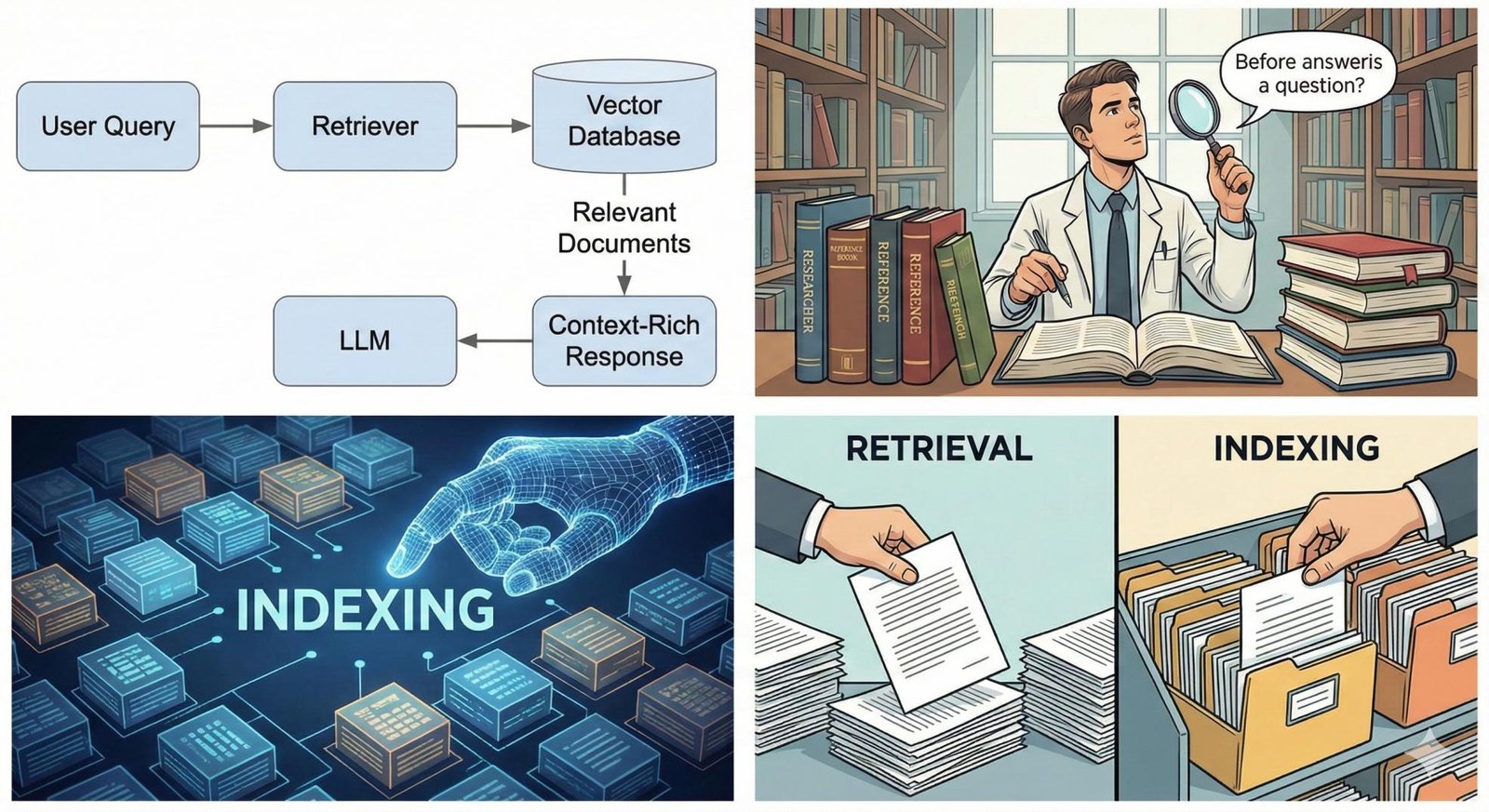
Demystifying RAG Indexing: Not Just Retrieval
A common misconception is that RAG is merely about retrieving relevant documents stored somewhere. But before retrieval can happen, the data must be properly organized or indexed to allow quick and precise fetching. Simply storing entire documents in a vector database without considering how the indexing is done is like putting all your files in one huge drawer — searching becomes slow, erratic, and ineffective.
What is Indexing then?
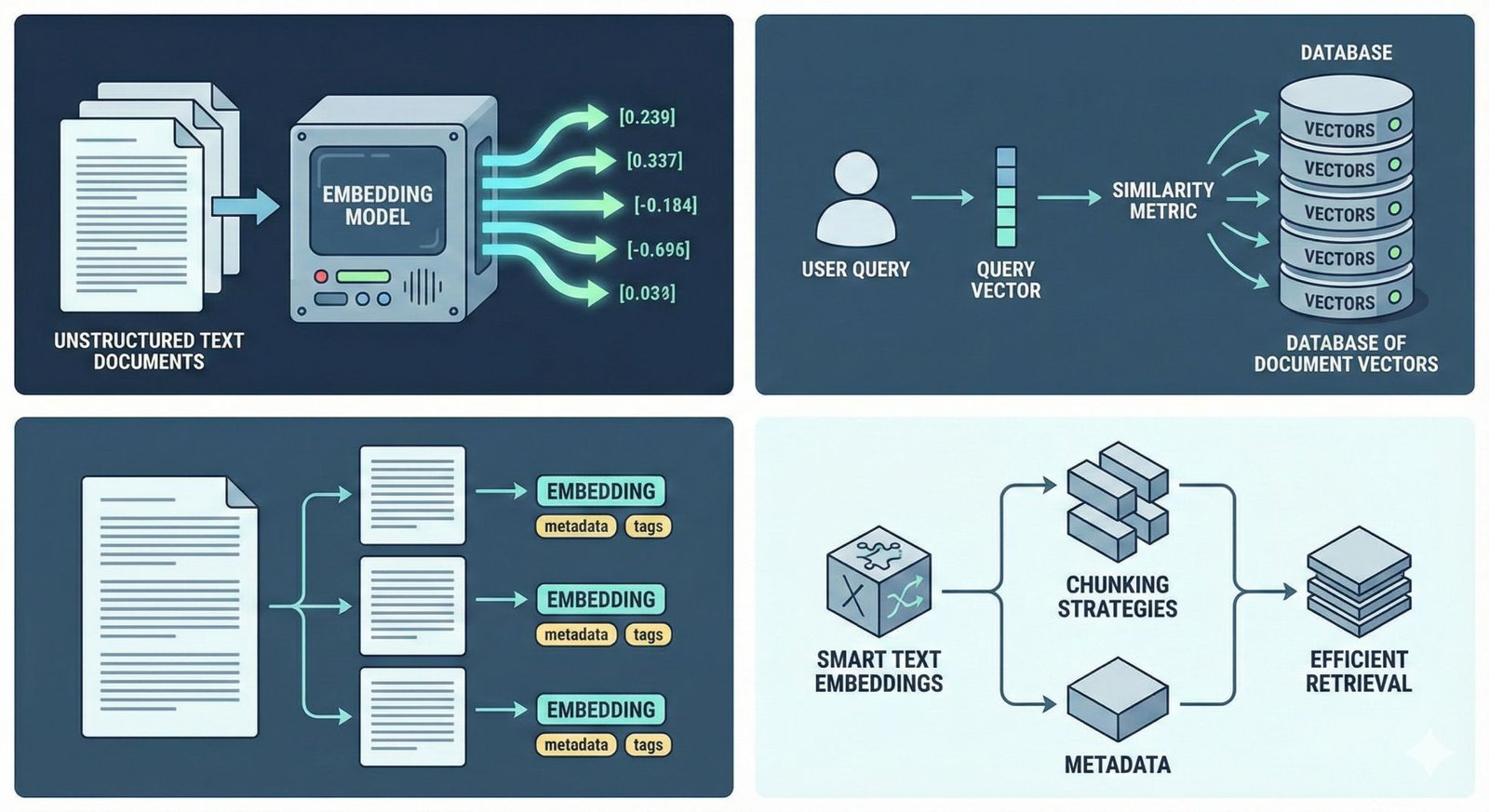
Indexing in RAG is the process of converting unstructured text documents into searchable representations, often vectors, that capture the semantic meaning of the text. This way, when a query is presented, the model can use similarity metrics to find which pieces of data are relevant and retrieve them quickly. Good indexing involves smart text embeddings, chunking strategies, and metadata to allow efficient retrieval later.
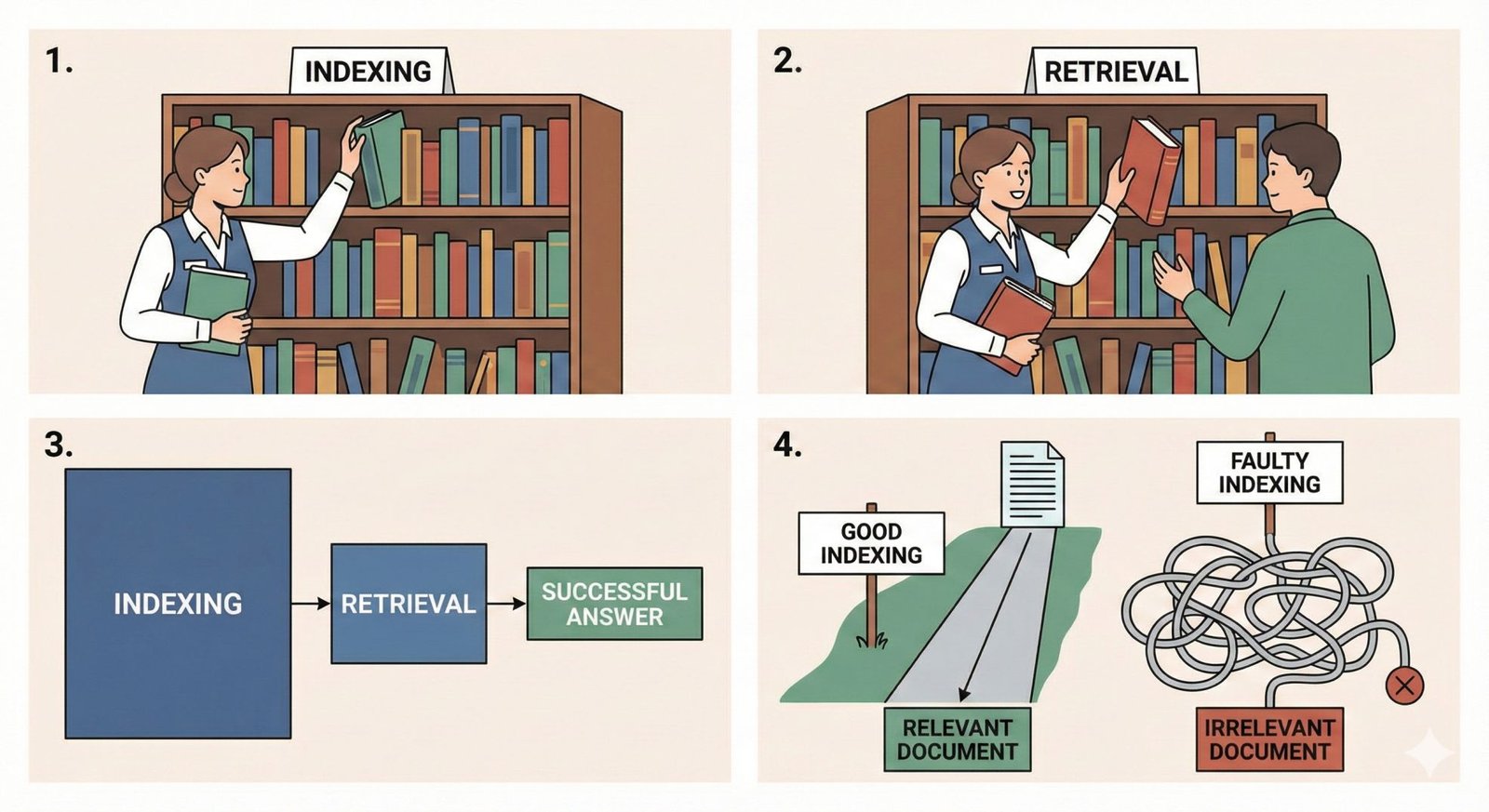
Indexing vs. Retrieval: Why Both Matter
Think of it like a library. Indexing is how the librarian organizes books by genre, author, or subjects with an easy-to-follow card system. Retrieval is the actual act of pulling the right book off the shelf when someone asks for it. Without proper indexing, even the smartest librarian would struggle to find the book fast. In RAG systems, faulty or shallow indexing results in irrelevant or missed documents during retrieval, thereby deteriorating the overall LLM response quality.
Key Components Behind Effective RAG Indexing
Several important factors contribute to efficient RAG indexing, especially for beginner AI developers interested in fine-tuning their LLM applications:
How RAG Indexing Enhances LLM Performance
By combining well-designed RAG indexing with retrieval, LLMs can answer questions with access to vast external data far beyond their original training. This enables real-time knowledge updates, domain-specific expert systems, and better factual correctness. Instead of hallucinating plausible but incorrect facts, the model grounds its generation on retrieved pieces of information. This revolutionizes use cases such as customer support bots, personalized recommendation engines, and research assistants.

Example Scenario: Customer Support
Imagine a chatbot assisting customers with technical product questions. Without RAG, the chatbot relies solely on pre-trained knowledge and can rapidly become outdated. With RAG indexing properly implemented, frequent product manuals, updated FAQs, and troubleshooting logs are vectorized and kept indexed. When a customer query arrives, the chatbot retrieves relevant up-to-date snippets and seamlessly weaves that information into its answer—making the AI support feel truly smart and reliable.
Before concluding “RAG Indexing” you may would like to see more posts on Artificial intelligence
Conclusion: Why Paying Attention to RAG Indexing Counts
Retrieval-Augmented Generation is much more than just grabbing documents out of a vector store—it’s about the intelligent organization of knowledge that enables LLMs to amplify their capabilities effectively. Indexing sets the stage for optimized retrieval, improved relevance, and overall better user experiences in AI applications. Whether you’re a beginner dipping your toes in LLMs or a developer designing complex AI assistants, investing time to understand and fine-tune RAG indexing will pay dividends. Ready to harness RAG to build smarter, more grounded AI systems? Explore advanced frameworks, experiment with embeddings, and start indexing your way to AI excellence.
Essential Resources for Your RAG Journey
The Theory: Read the original RAG Research Paper to understand the academic foundation.
The Practice: Follow the LangChain RAG Tutorial for a step-by-step code guide.
The Indexing: Explore Weaviate’s Blog to master vector search algorithms.